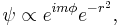Optical vortex
An optical vortex (also known as a screw dislocation or phase singularity) is a zero of an optical field, a point of zero intensity. Research into the properties of vortices has thrived since a comprehensive paper by Nye and Berry, in 1974,[1] described the basic properties of "dislocations in wave trains". The research that followed became the core of what is now known as "singular optics".
Contents |
Explanation
Light can be twisted like a corkscrew around its axis of travel. Because of the twisting, the light waves at the axis itself cancel each other out. When projected onto a flat surface, an optical vortex looks like a ring of light, with a dark hole in the center. This corkscrew of light, with darkness at the center, is called an optical vortex.
The vortex is given a number, called the topological charge, according to how many twists the light does in one wavelength. The number is always an integer, and can be positive or negative, depending on the direction of the twist. The higher the number of the twist, the faster the light is spinning around the axis. This spinning carries orbital angular momentum with the wave train, and will induce torque on an electric dipole.
This orbital angular momentum of light can be observed in the orbiting motion of trapped particles. Interfering an optical vortex with a plane wave of light reveals the spiral phase as concentric spirals. The number of arms in the spiral equals the topological charge.
Optical vortices are studied by creating them in the lab in various ways. They can be generated directly in a laser,[2] or a laser beam can be twisted into vortex using a "fork" computer generated hologram.[3] The "fork" hologram can be used in a spatial light modulator, a specialized type of liquid crystal display controlled by a computer; or in a diffraction grating on a film or piece of glass.
Properties
An optical singularity is a zero of an optical field. The phase in the field circulates around these points of zero intensity (giving rise to the name vortex). Vortices are points in 2D fields and lines in 3D fields (as they have codimension two). Integrating the phase of the field around a path enclosing a vortex yields an integer multiple of 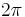 . This integer is known as the topological charge, or strength, of the vortex.
. This integer is known as the topological charge, or strength, of the vortex.
A hypergeometric-Gaussian mode (HyGG) has an optical vortex in its center. The beam, which has the form
is a solution to the paraxial wave equation (see paraxial approximation, and the Fourier optics article for the actual equation) consisting of the Bessel function. Photons in a hypergeometric-Gaussian beam have an orbital angular momentum of mħ. The integer m also gives the strength of the vortex at the beam's centre. Spin angular momentum of circularly polarized light can be converted into orbital angular momentum.[4]
Creation
Hypergeometric-Gaussian modes can be created with a spiral phase plate, computer-generated holograms, mode conversion, q-plate or a spatial light modulator.
Static spiral phase plates (SPPs) are spiral-shaped pieces of crystal or plastic that are engineered specifically to the desired topological charge and incident wavelength. They are efficient, yet expensive. Adjustable SPPs can be made by moving a wedge between two sides of a cracked piece of plastic.
Computer-generated holograms (CGHs) are the calculated interferogram between a plane wave and a Laguerre-Gaussian beam which is transferred to film. The CGH resembles a common Ronchi linear diffraction grating, save a "fork" dislocation. An incident laser beam creates a diffraction pattern with vortices whose topological charge increases with diffraction order. The zero order is Gaussian, and the vortices have opposite helicity on either side of this undiffracted beam. The number of prongs in the CGH fork is directly related to the topological charge of the first diffraction order vortex. The CGH can be blazed to direct more intensity into the first order. Bleaching transforms it from an intensity grating to a phase grating, which increases efficiency.
Mode conversion requires Hermite-Gaussian (HG) modes, which can easily be made inside the laser cavity or externally by less accurate means. A pair of astigmatic lenses introduces a Gouy phase shift which creates an LG beam with azimuthal and radial indices dependent upon the input HG.
A spatial light modulator is a computer-controlled electronic device which can create dynamic vortices, arrays of vortices and other types of beams.
At radio frequencies it is trivial to produce a (non optical) vortex. Simply arrange a half wavelength diameter ring of antennas such that the phase shift of the broadcast antennas varies an integral multiple of 2π around the ring.
q-plate
A q-plate is a birefringent liquid crystal plate with an azimuthal distribution of the local optical axis, which has a topological charge q at its center defect. The q-plate with topological charge q can generate a 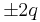 charge vortex based on the input beam polarization.
charge vortex based on the input beam polarization.
Applications
Extrasolar planets have only recently been directly detected, as their parent star is so bright. Progress has been made in creating an optical vortex coronagraph to directly observe planets with too low a contrast ratio to their parent to be observed with other techniques.
Optical vortices are used in optical tweezers to manipulate micrometer-sized particles such as cells. Such particles can be rotated in orbits around the axis of the beam using OAM. Micro-motors have also been created using optical vortex tweezers.
Current computers use electrons which have two states, zero and one. Quantum computing could use light to encode and store information. Optical vortices theoretically have an infinite number of states, as there is no limit to the topological charge. This could allow for faster data manipulation. The cryptography community is also interested in optical vortices, as they can communicate using a higher bandwidth of information. However, that will need further developments in optical fibers, since existing optical fibers change the twist of optical vortices when bent or stressed.
Twisted radio beams could reduce radio-frequency congestion by using the large number of vortical states,.[5][6]
References
- ^ Nye, J. F.; and M. V. Berry (1974). "Dislocations in wave trains" (PDF). Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A 336 (1605): 165. doi:10.1098/rspa.1974.0012. http://www.hep.princeton.edu/~mcdonald/examples/mechanics/nye_prsla_336_165_74.pdf. Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- ^ White, AG; Smith, CP; Heckenberg, NR; Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H; McDuff, R; Weiss, CO; Tamm, C (1991). "Interferometric measurements of phase singularities in the output of a visible laser". Journal of Modern Optics 38 (12): 2531–2541. Bibcode 1991JMOp...38.2531W. doi:10.1080/09500349114552651.
- ^ Heckenberg, NR; McDuff, R; Smith, CP; White, AG (1992). "Generation of optical phase singularities by computer-generated holograms". Optics Letters 17 (3): 221–223. Bibcode 1992OptL...17..221H. doi:10.1364/OL.17.000221. PMID 19784282.
- ^ Marrucci, L.; Manzo, C; Paparo, D (2006). "Optical spin-to-orbital angular momentum conversion in inhomogeneous anisotropic media". Physical Review Letters 96 (16): 163905. Bibcode 2006PhRvL..96p3905M. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.163905. PMID 16712234. http://link.aps.org/abstract/PRL/v96/e163905.
- ^ Twisted radio beams could untangle the airwaves
- ^ Utilization of Photon Orbital Angular Momentum in the Low-Frequency Radio Domain
External links
- Optical vortices and optical tweezers at the University of Glasgow
- Singular Optics Master list by Grover Swartzlander Jr., University of Arizona, Tucson
- Optical vortex coronograph, Gregory Foo, et al., University of Arizona, Tucson
- Optical tweezers, David Grier, NYU
- Selected Publications on Optical Vortices at Australian National University
- "All Screwed Up: Scientific American article". http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?articleID=000F16C0-C84F-1FA2-884F83414B7F0000.
- "'Twisting' light packs more information into one photon: New Scientist article". http://technology.newscientist.com/article/dn13522-twisting-light-packs-more-information-into-one-photon.html.
- "Light Beams in High-Order Modes". http://departments.colgate.edu/physics/research/optics/oamgp/gp.htm.
- "Twisted Light Encryption". http://www.unc.edu/~jmspille/187/assign4_forecast.html.
- "Twisted Physics: Scientists Create Knots of Light". Fox News. 2010-01-18. http://www.foxnews.com/scitech/2010/01/18/twisted-physics-scientists-create-knots-light/?test=latestnews.